Business Process Management¶
The Business Process Management (BPM) tool provides the ability to model and automate business processes in EspoCRM in a no-code/low-code way. The engine executes business processes described in the BPMN 2.0 standard.
The BPM tool is available in Advanced Pack extension.
Difference from Workflows tool¶
The Workflows tool is intended for automation of simple business rules, without sequential flow items, when there is no need to display the flow graphically.
The BPM tool is intended for more complex business logic, where there can be diverging and converging flows, execution delays, user interactions. The flowchart view makes the business process more comprehensible for a human, the log allows to see how the process was held.
The BPM tool has all the capabilities of the Workflows tool. If you've used the Workflows tool before, your knowledge will be useful for getting into BPM, as they share a number of features.
In this article:
See also¶
- Examples
- Signals
- Compensation
- BPM specific formula functions
- Drip Email Campaign with BPM
- Tracking URLs with BPM
- Tips
- Configuration
Process Flowcharts¶
Available under Administration > Flowcharts. An administrator can also add the Process Flowcharts tab to the navigation bar.
Flowcharts are intended for modeling business processes. An administrator can create and edit flowcharts. Regular users can only view flowcharts.
Every Flowchart has its specific entity type (defined by the Target Type field). The Flowchart determines execution of future process instances. It comprises flowchart elements and connections between elements.
If a Process Flowchart has the unchecked Is Active field, then it won't initiate process instances.
To show details and parameters of a certain flowchart element you need to click on it. In the edit mode you will be able to edit parameters.
Processes¶
Available under Administration > Processes. An administrator can also add the Processes tab to the navigation bar.
A Process represents a business process instance. When it's initiated, it gets the status Started. When the Process is finished, it gets the status Ended.
A Process is executed according to its Flowchart. The Flowchart of a Process can't be changed after the Process is started.
A Process is obligatorily related to a single target record.
Processes can be started:
- Automatically – Upon specific conditions, signal, or scheduling, described in the Flowchart.
- Manually – To start process manually, a user needs to click the Start Process button on the Processes list view, or on the record detail view from the dropdown in the top-right corner.
- By a Workflow rule – using the Start BPM Process action in a rule. It allows to pass the workflow's target record or a related record as a target for the new process.
By using a Workflow with the manual trigger, it's possible to have a button on the detail view that will start a particular process.
The execution of a Process is visualized with colors highlighting statuses of flow nodes:
- green – processed;
- yellow – pending;
- violet – in process;
- gray – failed.
Only one Process for the same target record and Flowchart can be active at the same time. It means that if you have multiple Start Events, once one of them is triggered (the process is started), other Start Events will be ignored while the Process is active.
Usually Processes start their execution flow from a Start Event (green colored circle). One Process Flowchart can have multiple Start Events.
Manipulating¶
A Process can be stopped manually by a user who has edit access to that Process. You can do it from the dropdown menu next to the Edit button.
It's possible to manually reject or interrupt pending and active flow nodes. You can do it from the Log panel on the Process detail view in the dropdown menu of a specific Flow Node. Note that in some cases after rejecting a Flow Node the Process becomes suspended and won't ever end by itself. You will need to either manually stop it or start a flow from any node to continue executing.
It's possible to manually start a flow from any element of an already started Process. You need to click on a specific flowchart element on the Process detail view and then click the button Start flow from here.
Ended, stopped and interrupted Processes can be reactivated (from the dropdown next to the Edit button). After reactivation, the Process does not have any active Flow Nodes. You need to manually start the flow from a specific Flow Node element. Ended Sub-Processes can be reactivated only if their parent Process is active. Meaning that you might need to reactivate the parent Process first.
Access control¶
Only administrators can create or edit Flowcharts. With Roles it's possible to allow regular users to view Flowcharts, and view or edit Processes. Note that a user needs also to have access to the Process Flowchart scope to be able to view Process Flowchart details.
Flowchart Elements¶
See more detail in separate articles:
Gateways¶
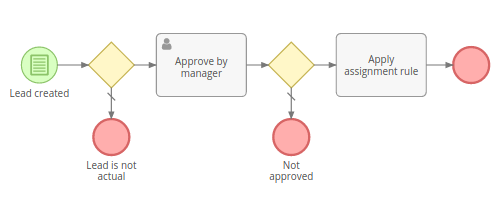
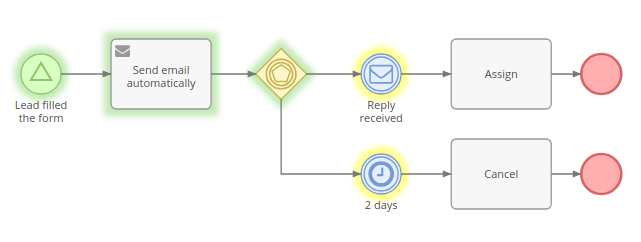
Gateways diverge and converge flows. Depicted as a yellow diamond. They can be used to determine a path in which the flow will go depending on specific conditions. They can split the flow into multiple parallel flows and join parallel flows into a single one.
Events¶
Events represent something that happens during a business process. They also start, end and interrupt the process flow. Depicted as a circle.
Activities¶
Automated tasks, manual tasks and sub-processes. Represented as a gray rectangle.
Flows¶
Sequence Flow¶
Represented as a solid arrow. It indicates the order in which process elements will be executed.
Conditions¶
Conditional events, exclusive and inclusive diverging gateways have conditions that determine the flow of the process.
Through the UI, there is the ability to check conditions for the following records:
- Target record;
- Records related to the target through many-to-one and children-to-parent relationships;
- Records created by the Process via tasks;
- User Task records, what allows checking a task resolution.
It's also possible to define conditions with Formula expressions. Example: status == 'New' && assignedUserId == null.
Conditions in the BPM tool are the same as in the Workflow tool. See more details about workflow's conditions.